SCROT doesn’t overwrite files: This is how to change that!
03/01/2023 (1433x read)
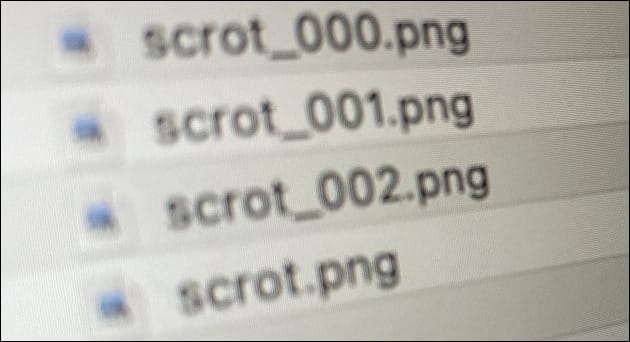
By default, the Linux screenshot tool scrot in newer versions doesn’t overwrite an existing file, even if you specify a filename. Instead, it creates a new file with an appended number, such as _000, _001, or _002. However, there is an easy way to make scrot overwrite the existing file with the given filename. This is particularly useful if you want to replace an old screenshot with a new one.
To achieve this, simply add the -o option (for „overwrite“) followed by the filename to the scrot command. For example:
scrot -o screenshot.png
This will capture the screenshot and save it as „screenshot.png“, overwriting any existing file with that name. Re-running the command will still save the image as „screenshot.png“ and not „screenshot_000.png“ or „screenshot_001.png“.
It’s worth noting that scrot has other useful options, such as the ability to capture a specific window or a selected region of the screen. You can explore these options by typing „man scrot“ in the terminal to access the manual page for the command.
In summary, adding the -o option to the scrot command will ensure that it overwrites any existing file with the same name, allowing you to keep your screenshot directory clutter-free.